The Science Behind Molecular Hydrogen
The Free Radical Theory Of Aging
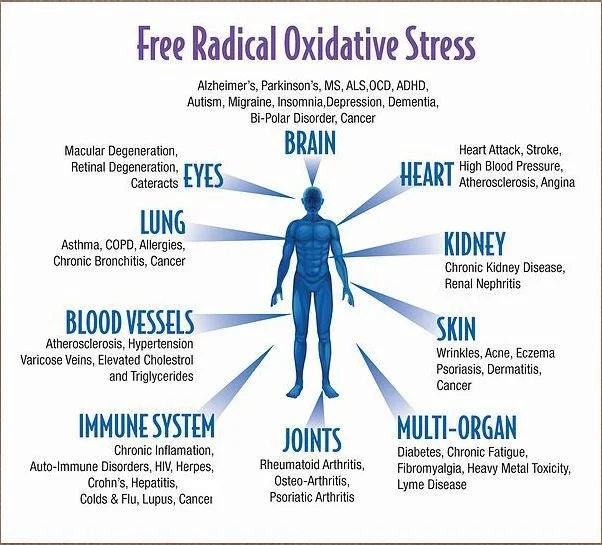
Free Radicals cause damage to our cells, particularly oxidative stress and this is what cause our bodies to age. As we age, our internal defense system declines, allowing oxidative stress to accumulate and resulting in cell damage, disease and finally death.
Free Radicals & Oxidative Stress
Free radicals are missing an electron and attack healthy cells in order to stabilize. Whether it is through essential metabolic processes within the body (mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, etc.) or from external sources (pollution, alcohol, heavy metals, pesticides, etc.), in today’s modern world we are constantly exposed to free radicals and there damaging effects on our bodies. The more this occurs, the more oxidative stress builds up which makes us more susceptible to disease.
Most Harmful Free Radicals To Our Bodies: Hydroxyl Radical & Peroxynitrite
These two free radicals are the most dangerous. Their insatiable need to survive by stealing and electron is so powerful that they attack healthy DNA, protein and lipids. This causes irreversible damage to the cells causing increasing health challenges and disease.